Master Plan Preparation for Cox’s Bazar District
(1st Revised) Project
Project Description
The Master Plan Preparation for Cox's Bazar District involved creating a Detail Area Plan (DAP) for the Cox's Bazar Development Authority (CoxDA). However, field surveys revealed significant discrepancies, with the actual on-ground measurement being larger than the Gazetted figure. To improve accuracy, Land Information System (LIS) data was collected, and Temporary Bench Marks (TBMs) were installed to ensure precise demarcation. Challenges faced included hilly terrain, flooded areas, shifting ground patterns, and coastal erosion.
Key Objectives
i. To define the CoxDA jurisdiction area in accordance with the official gazette
notification and field verification results.
ii. To establish an accurate GIS-based cadastral database, considering proper
land use planning, infrastructure development, and land management.
iii. To provide a legally and technically sound jurisdictional boundary for
future development control and governance under CoxDA.
iv. To prepare an official jurisdiction map for CoxDA, which will be used for
urban planning and policy-making.
Key Findings
i. The actual demarcated area (1,159.20 sq. km including sea beach) is significantly
larger than the gazetted
area (690.67 sq. km), revealing a discrepancy of nearly 468.52 sq. km due to
inconsistencies in mouza maps and gazette data.
ii. Only 8% of mouza areas matched the gazetted size, while 62% were larger and
30% were smaller,
indicating widespread map distortions, duplicated plots, and scale mismatches.
iii. Edge-matching errors, overlapping/underlapping boundaries, and plots
crossing international
boundaries complicated accurate demarcation and required extensive cadastral
adjustments and field verification.
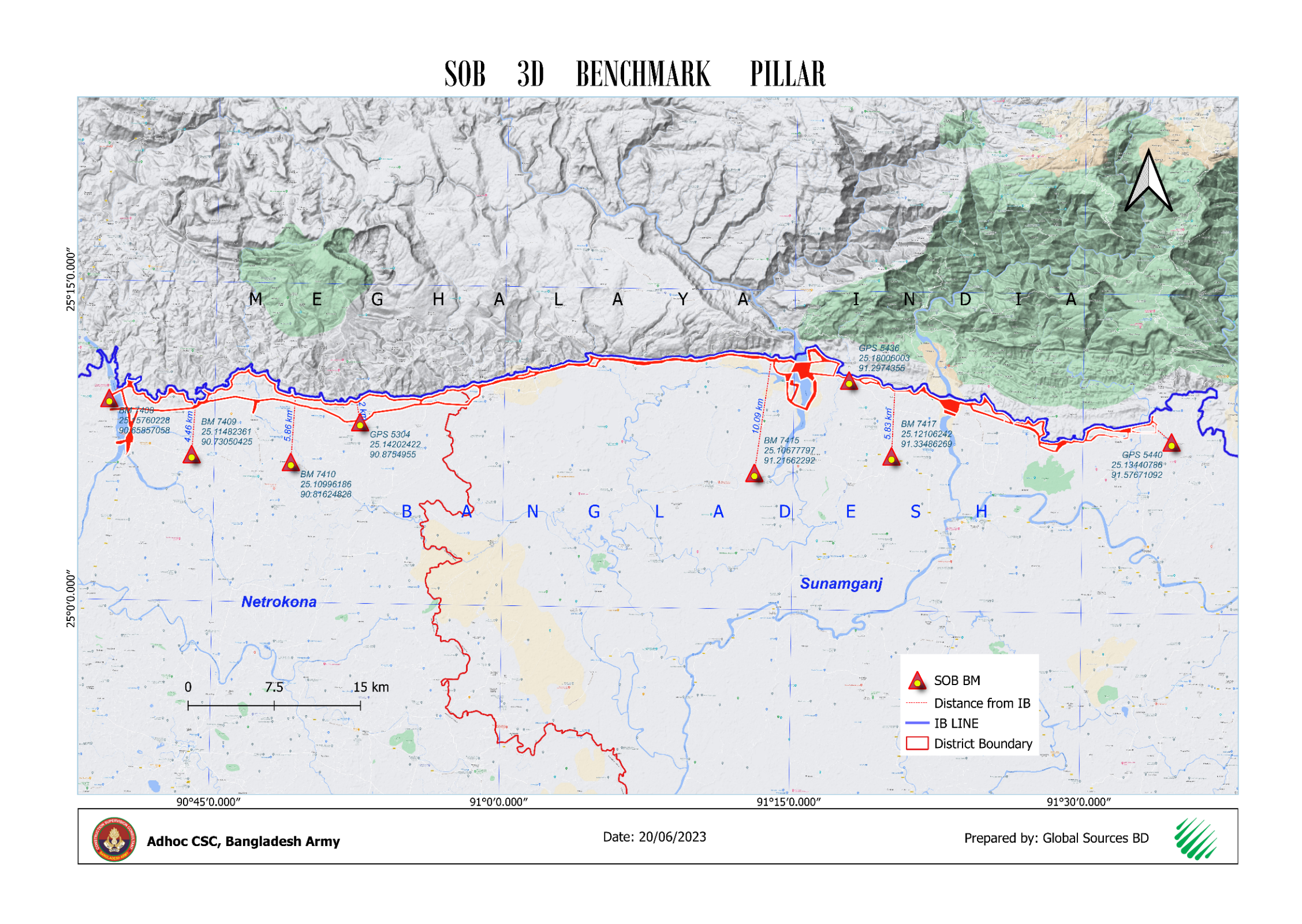
iv. 50 high-accuracy Temoporary Benchmarks (TBMs) and 4 CORS stations were
established to improve spatial
accuracy and provide reliable geodetic control for future surveys and mapping.
v. A Land Information System (LIS) database was prepared, identifying 618.46
sq. km
of government land from 40,980 plots, despite challenges from outdated, damaged, or
missing land records.
vi. The final jurisdiction map, based on adjusted cadastral data and validated
benchmarks, serves as a
technically sound and legally defensible boundary for planning and governance, but
highlights an
urgent need to revise official gazette records.
International Boundary Strip Map Georeferencing and International Boundary Digitization
Project Description
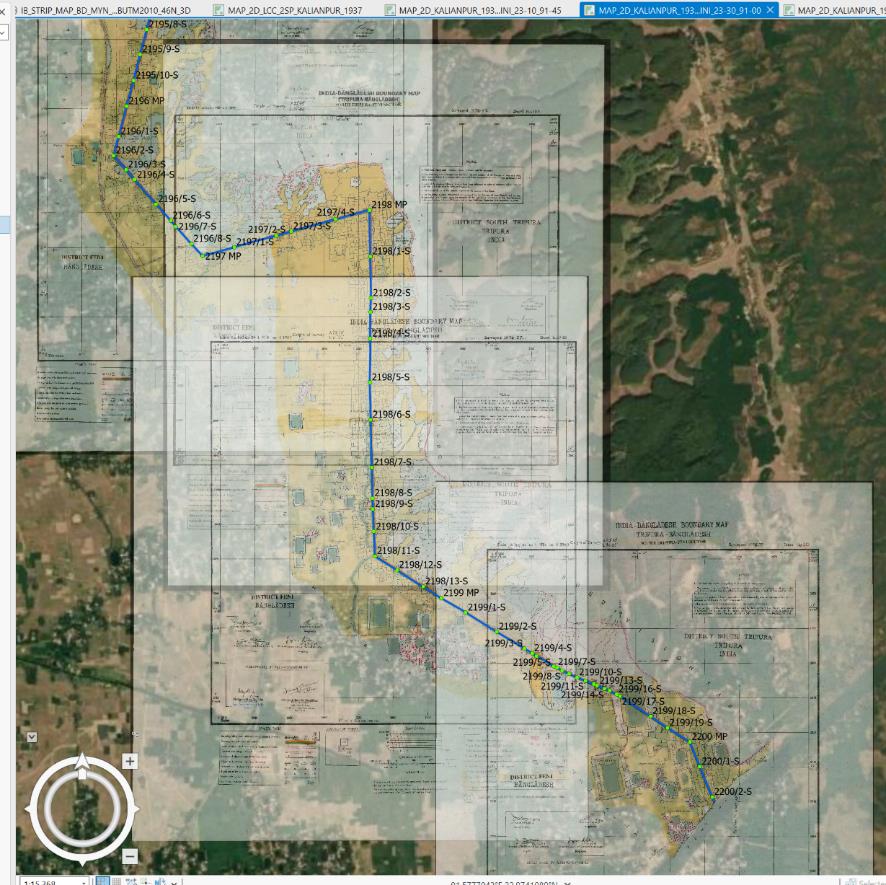
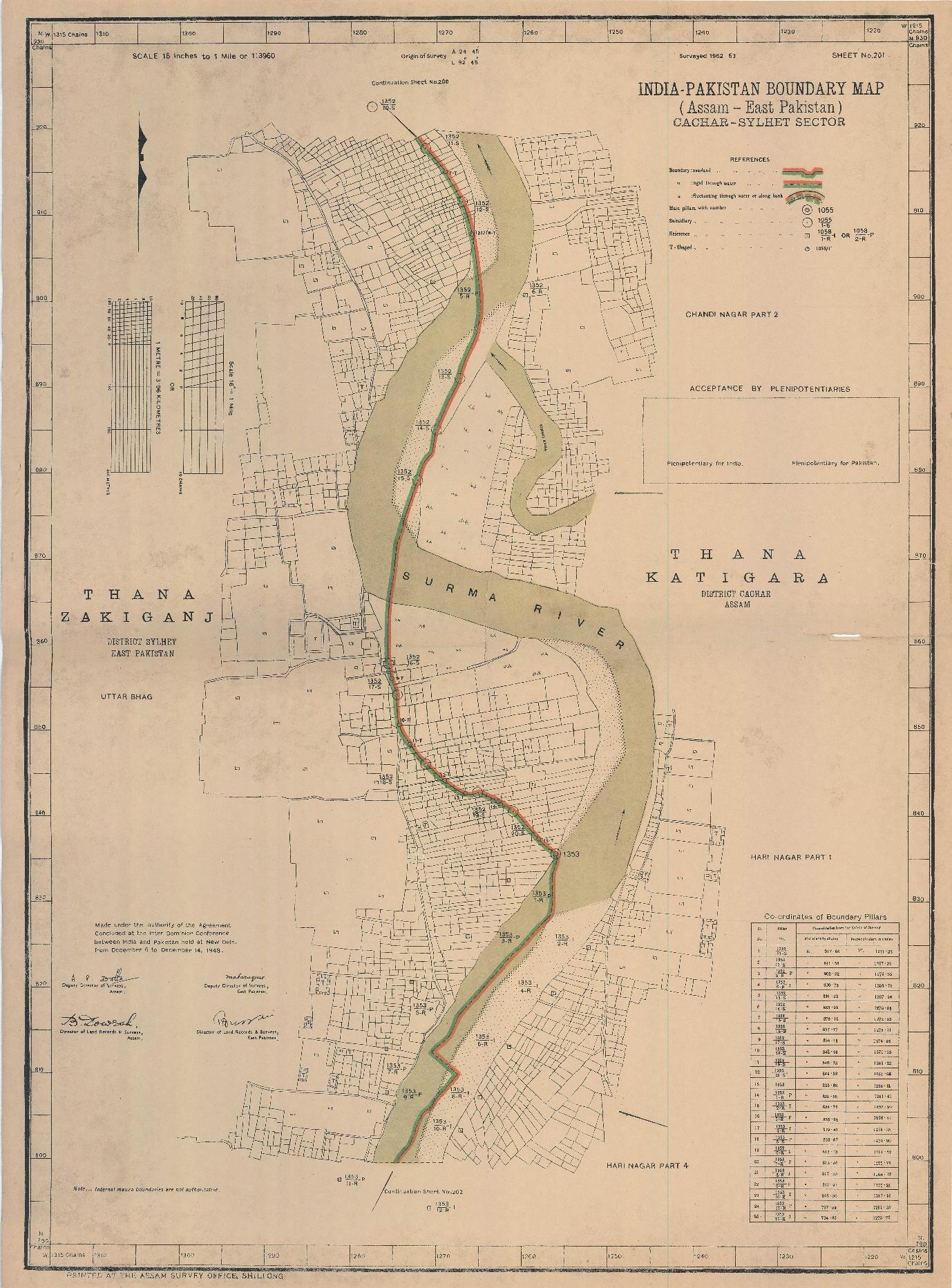
GSBD recently worked for 34 Construction Brigade, Bangladesh Army for International Boundary Line Digitalization using Border Strip map for India & Myanmar part. For IB line data, the strip map (International Boundary Map drawn with broth party agreement) were collected and georeferenced on the projection system the map sheets were produced that is Lambert Conformal Conic (LCC), 2 Standard Parallel, Everest 1830 (Adjustment 1937) ellipsoid, Kalianpur datum at Mizoram and Myanmar portion and Cassini Grid, Everest 1830 (Adjustment 1937) ellipsoid, Kalianpur datum at Tripura, Meghalaya, Assam portion of India. The data was then transformed into BUTM 2010 and WGS84 UTM 46N to make is useable in GNSS platform using the transformation parameters of Kalianpur 1937 datum to WGS 84 datum. At the same time, International Boundary Pillar means Internation GCP also digitized according to International Strip Map with same projection parameter.Key Objectives
i. Georeference and digitize the International Boundary Strip Maps for both the
Bangladesh–India and Bangladesh–Myanmar borders
using precise geodetic parameters for accurate boundary delineation.
ii. Collect and process UAV and satellite imagery data (including DEM and
orthophotos) to support the alignment of border
roads and map updated road networks in Cox’s Bazar, Bandarban, Rangamati,
Khagrachhari, and Chattogram districts.
iii. Digitize International Boundary Pillars and establish accurate
GNSS-compatible boundary data through
transformation into BUTM 2010 and WGS84 UTM 46N for future geospatial applications
and infrastructure development.
Key Findings
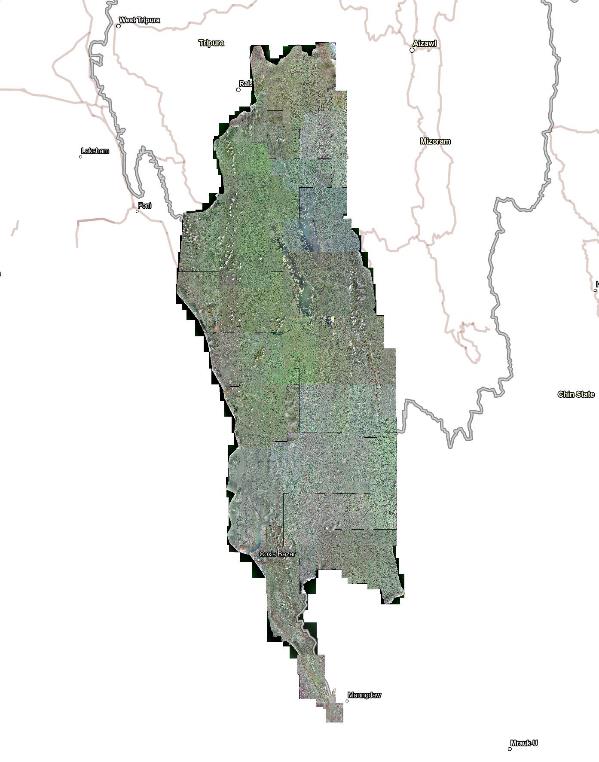
i. A total of approximately 22,230 sq. km of satellite imagery was successfully
processed, producing high-resolution orthophotos,
point clouds, and DEMs (using WorldView-3 imagery with 30cm GSD) for comprehensive
mapping coverage of the target districts.
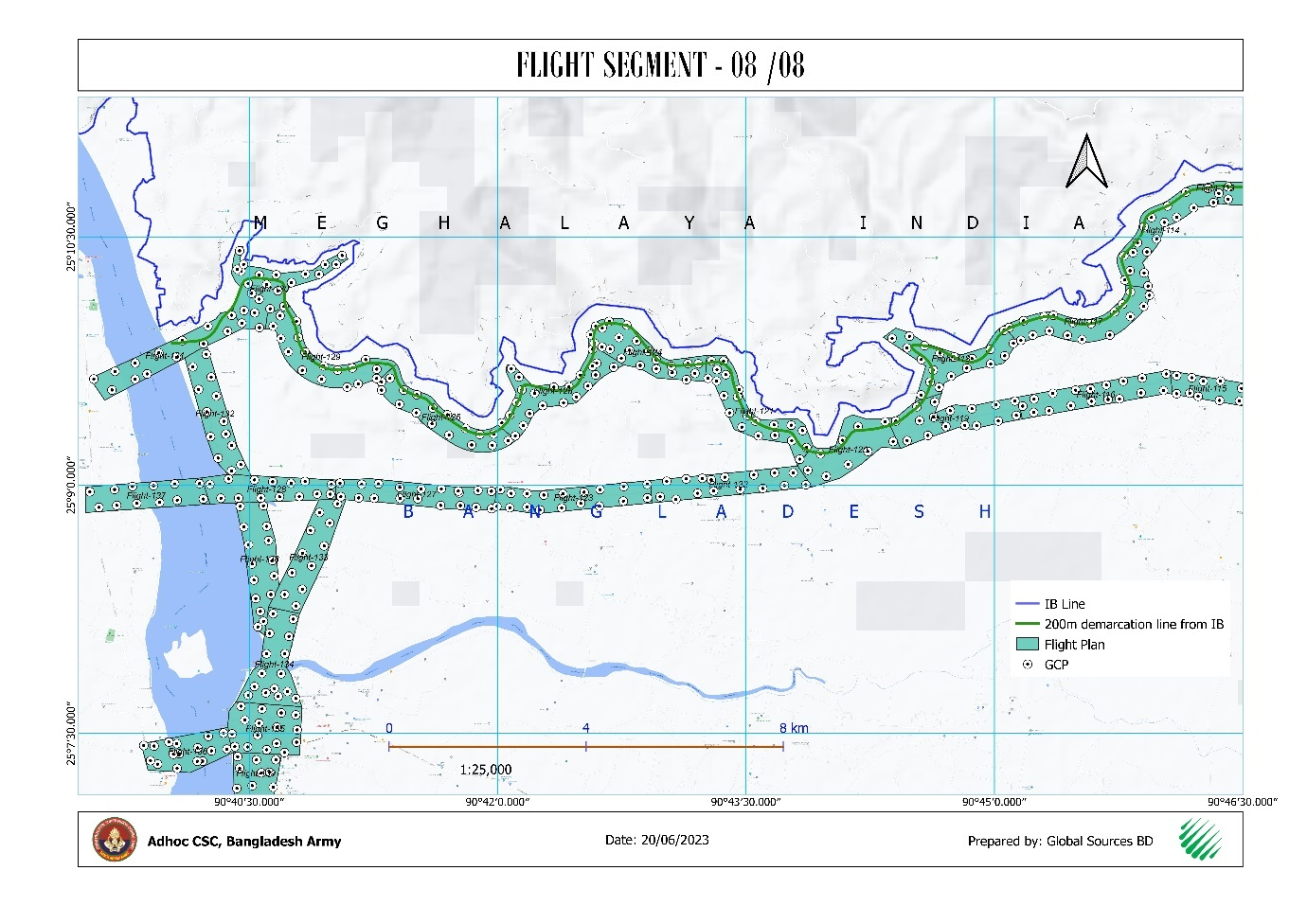
ii. The entire International Boundary Line from Gundum (Bandarban) to Volaganj
(Sylhet) was accurately digitized based
on georeferenced strip maps, ensuring alignment with historical treaties and
official boundary agreements.The entire International
Boundary Line from Gundum (Bandarban) to Volaganj (Sylhet) was accurately digitized
based on georeferenced strip maps, ensuring
alignment with historical treaties and official boundary agreements.
iii. The updated road networks for Khagrachhari, Bandarban, Rangamati, and Cox’s
Bazar districts were digitized, improving
the geospatial database to support border road connectivity and infrastructure
planning along the sensitive international border zones.
Satellite Image Processing of Five districts
Scope of Work
GCP Collection of the five districts comparing the captured satellite image
permanent structure with present structure on the earth surface.
Incorporation of Collected GCPs and filtering for Processing Satellite Image.
Conducting Aerial Triangulation (AT) with GCP in Photogrammetry processing
Software.
Producing and editing DEM from the Sterio satellite image.
Processing and creating Orthorectification of the image and prepare orthophoto
with required GSD (30 cm)
Key Findings
i. Processed about 22,230 sq km of Satellite image for Chattogram, Khagrachari,
Bandarban, Rangamati & Cox’s Bazar
district and preparing Orthophoto, point cloud and DEM from using World View-3
Satellite imagery of 30cm GSD
ii. Editing the DEM to make it usable for further any processing and data
extraction
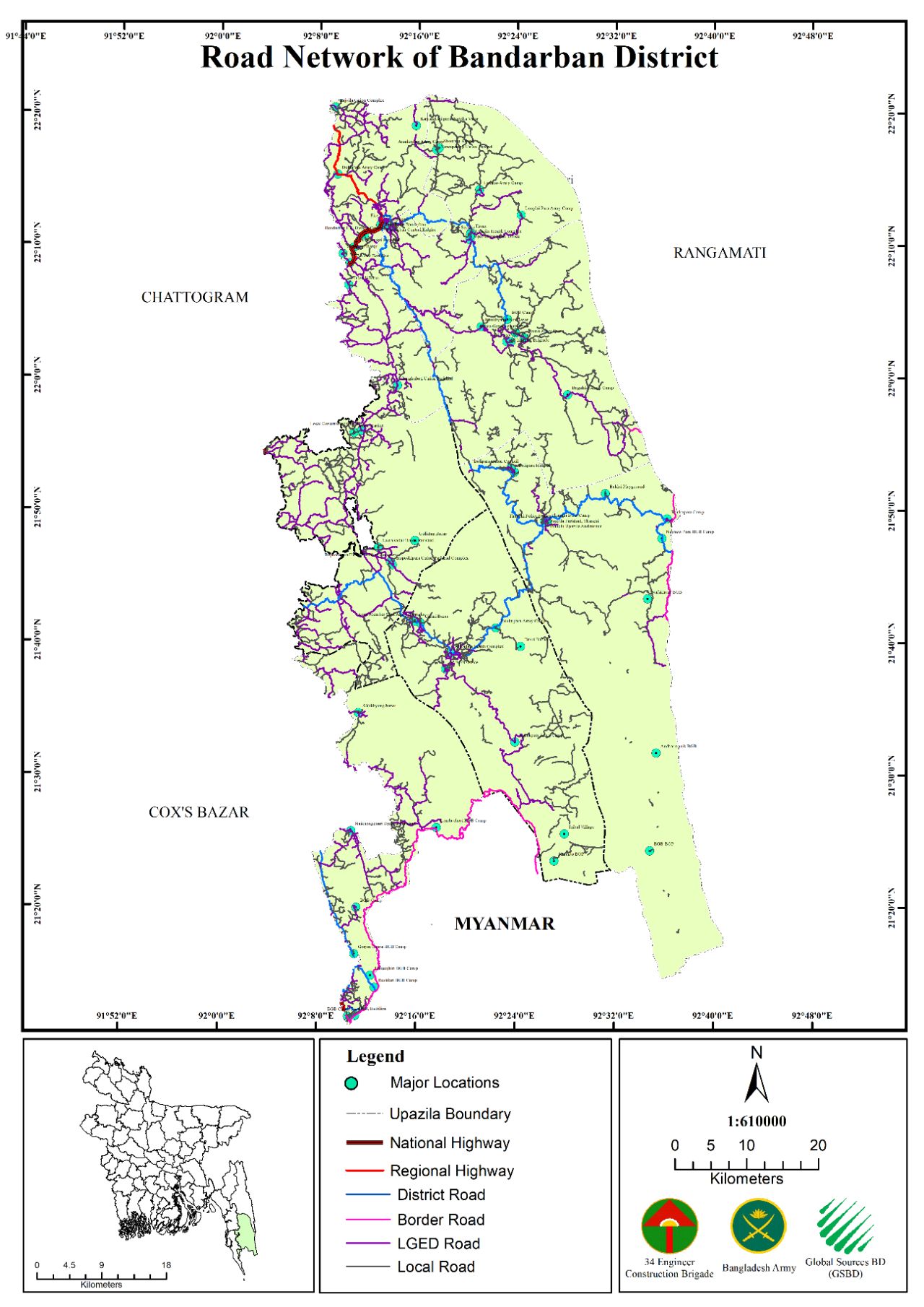
Road Network of Cox’s Bazar, Bandarban, Rangamati, Khagrachhari District
Scope of Work
Survey of existing road of Cox's Bazar, Bandarban, Rangamati, and Khagrachhari district with RTK GNSS and collection of road inventory data like length, width, type and Ownership of the road etc.Road Network digitization and mapping for Border Road Connectivity in Cox's Bazar, Bandarban, Rangamati, Khagrachhari and Chattogram district using processed Satellite image for the Hill-districts.
Key Findings
i. Digitized updated road network for, Khagrachari, Bandarban, Rangamati & Cox’s
Bazar district.
ii. Updating digital database of road network showing the connectivity with
border road of four hill-districts.
Feasibility Study for Sunamganj-Durgapur Border Road Project
Project Description
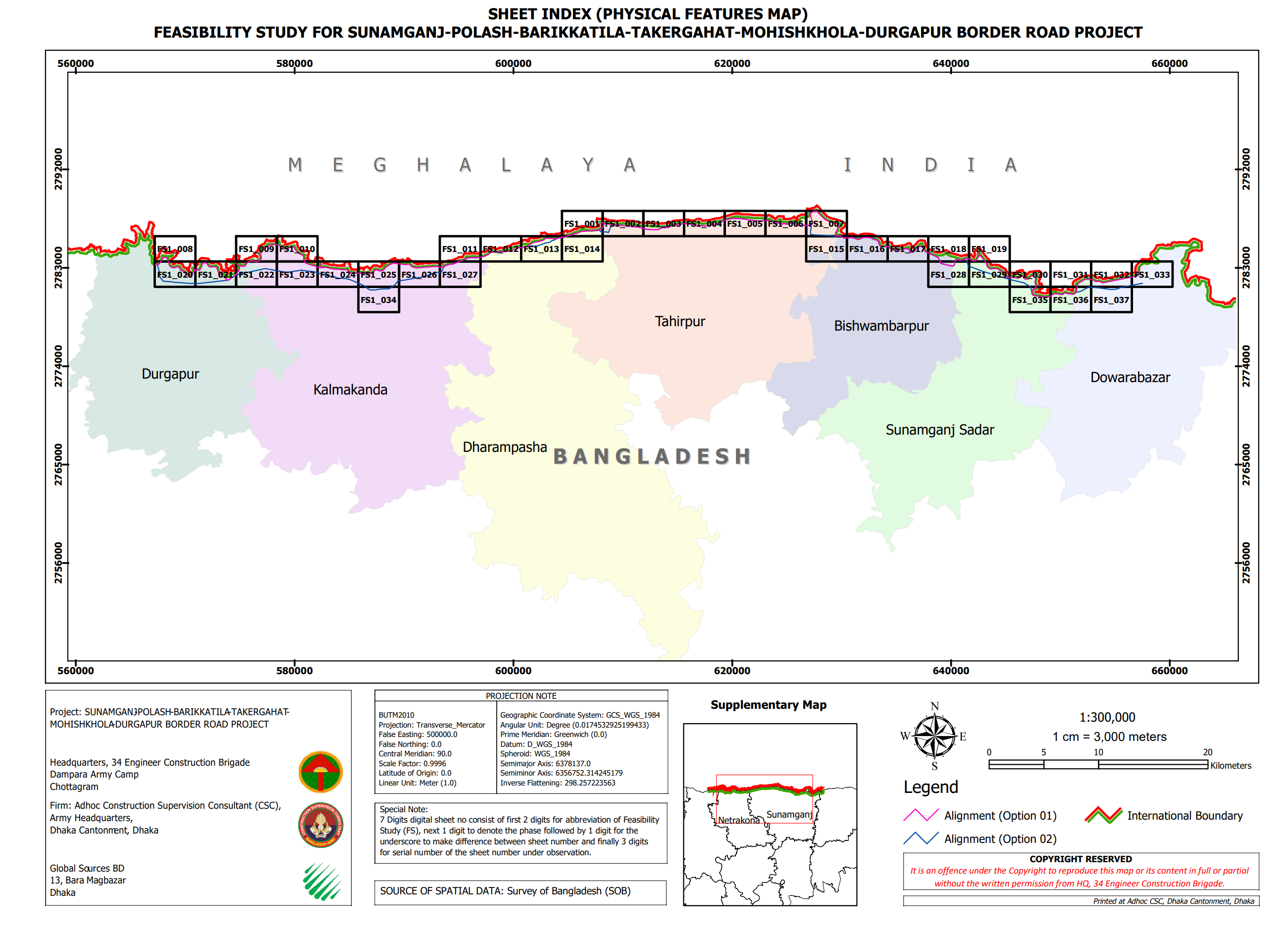
The proposed feasibility study project for the Sunamganj-Polash-Barikkatila-Takergahat-Mohishkhola-Durgapur border road in the Northern part of Netrokona and Sunamganj districts of Mymensingh and Sylhet division aims to improve connectivity and security along the Meghalaya border with India. The area, which has a rich tourism scene, faces challenges such as poor connectivity, inadequate road infrastructure, and socio-economic issues. The aerial survey aimed to understand topography, hydrology, environmental impact, socio-economic events, traffic situation, alignment fixation, and the suitability of the border road from the international boundary. The survey covered 117.7 km and covered 53.31 square kilometers. The area is rich in stones and sand, with potential for growth and traffic.
Key Objectives
i. Aerial Survey for fixation of alignment and mapping
ii. Topographical Investigation for fixation of profiling.
iii. Identification of High-Water Level, Low-Water Level, Scour Depths and Bed
Conditions.
iv. Preparation of Initial Environmental Scoping Report (IESR)
v. Forecasting future traffic generation with and without construction of the
new road.
Key Findings
i. Return of Original hardcopy mouza maps
ii. Processed orthophoto mosaic map of the project area with 2cm GSD
iii. Digitized Physical Feature data with Attribute
iv. Georeferenced Mouza map sheet (softcopy)
v. Digitized Land parcel data base (plot database) of mouza maps along the
project area.
vi. Physical Feature map overlying on digitized mouza map data.
vii. Existing Land use digital database
viii. Produced Land Acquisition maps and Land use maps
ix. Mouza plot schedule for Land acquisition and physical feature
Feasibility Studies for Border Road Construction Project from Gundum to Volaganj
Project Description
The 2nd phase border road alignment in Bangladesh was developed using recce data and SoB IB line and pillar data, considering the country's border road alignment criteria. However, complexities arose due to some area crossing the IB line at the Myanmar part. A strip map was collected and georeferenced, and the data was transformed into BUTM 2010 using the Kalianpur 1937 datum. A unique difference of about 3.5 meters was found between the SoB pillar data and transformed strip map IB pillar data. The alignment map was updated for the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd phases. A DEM, spot-height, and contour line were produced along the alignment, covering 458.80 sqkm.
Key Objectives
i. Developing the alignment for 2nd phase border roads along the IB line and
terminal roads.
ii. Preparing the DEM along the alignment and IB line with 1km width.
iii. Preparing Spot Height at 10m Grid interval from the DEM.
iv. Preparing the Contour Line at 5m and 10m interval from the DEM / Spot
height.
Key Findings
i. Fixing road alignment in hilly terrain (peaks up to 1014m, low points at -2m MSL)
near international borders required careful
planning and GNSS/GIS-based surveys.
ii. Strip maps revealed discrepancies in IB pillar coordinates due to differing
datum transformations (Kalianpur 1937 vs.
Gulshan 303), causing shifts of ~3.5m.
iii. Sections of the 1st phase road were found crossing the IB line (Myanmar
side), necessitating corrections using
strip maps for accurate border representation.
iv. The 2nd phase alignment length grew from an estimated 360 km to 456.8 km,
with DEM, contours, and maps generated for planning.
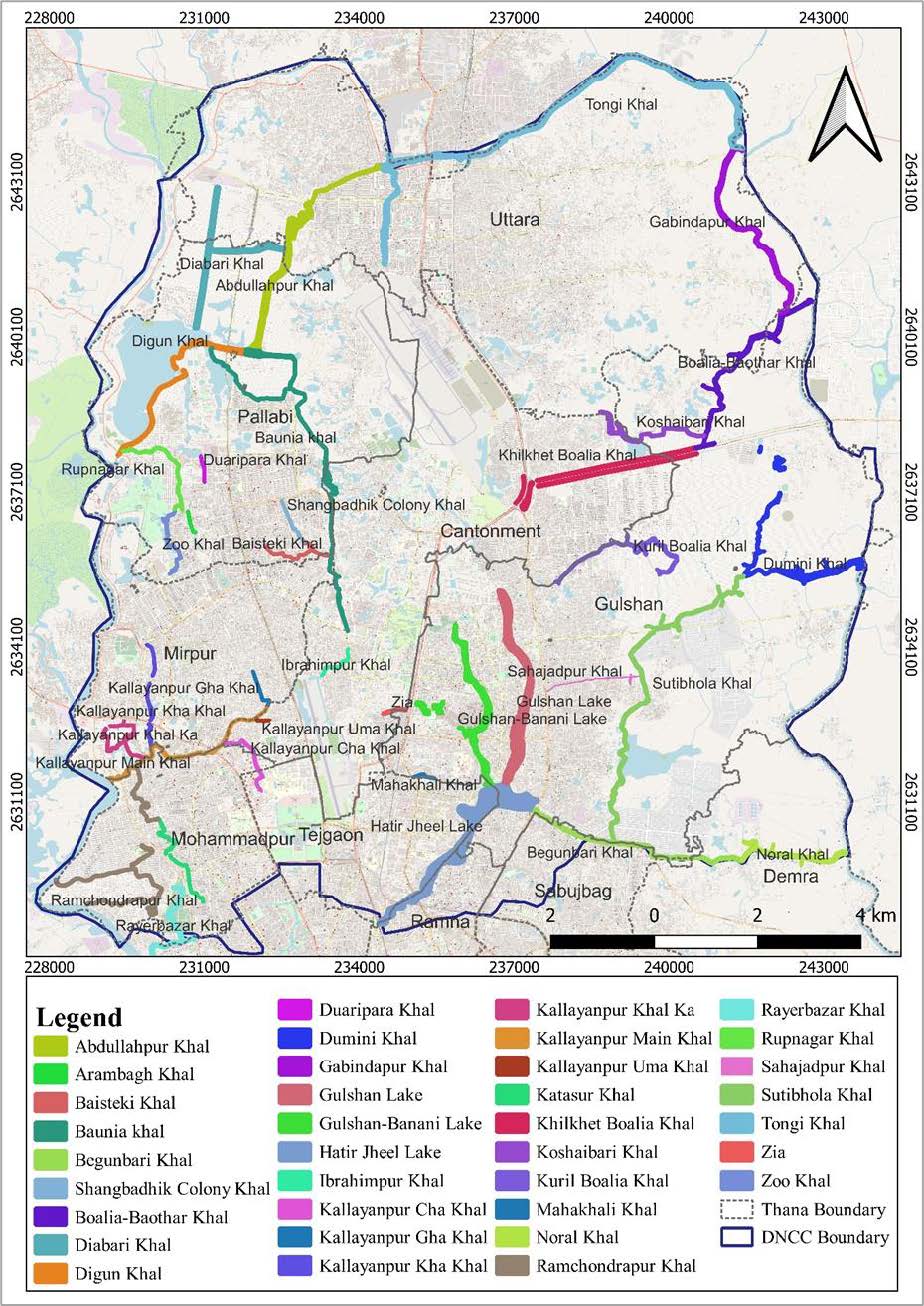
Boundary Demarcation and Pillar Construction of DNCC 29 Khal and 1 regulating pond, Evacuation of Illegal Occupancy and GIS Database Preparation of the Khal and Pond Project
Project Description
Mouza maps of three different time period Cadastral Survey (CS) (1888 - 1940), Revenue Survey (RS) (1967-1982) and Mohanogor Survey (MS) (1995-2004) of the ten thanas have been collected, geo-referenced and digitized. Advanced GPS (Global Positioning System) and Real-time kinematic positioning (RTK) based survey technique and drone survey used for Physical Features and Orthophoto generation. The Khal position in CS or RS or MS was not clearly known where it is matching to actual ground location. So, the maps of these three-time period were aligned. The Khals position are found different from the existing Khals. The not matching situation exists due to changes of land topography, urbanization, illegal occupation etc. So Mouza Maps of this period were aligned, georeferenced and digitized to determine the change of Khal length, width, area and boundary over the time for demarcation of 29 khals and 1 regulating pond of DNCC area.
Key Objectives
i. Capturing of aerial imagery of total area of approximate 12000 acres using survey
grade UAV including data processing,
ortho-photo preparation for the City Zorip (MS), RS and CS Mouza Sheet Ground
adjustment.
ii. Establishment of Ground Control Points (GCP) for aerial survey and Mouza
Sheet using RTK GNSS.
iii. Georeferencing CS, RS and MS Mouza Map sheet along the 29 Khal and one
Retention Pond area for delineating Khal and Pond boundary.
iv. Digitizing of the Legal Boundary of the Khal and preparing GIS database.
v. Identification and digitization of areas of illegal occupation including
features and attributes within the legal Khal boundary.
Key Findings
i. Processed orthophoto mosaic map of DNCC Khal area (more than 12000 acre) with 2cm
GSD.
ii. Established GCP database.
iii. Georeferenced CS, RS and MS Mouza maps (softcopy).
iv. Digitized legal Khal boundary and one retention pond boundary GIS database
according to CS, RS and MS mouza map and Dhaka WASA LA case.
v. Identified illegal occupancy point database.
vi. Point database for source of pollution to the Khal of DNCC.
Padma Bridge Rail Link Project (PBRLP)
Scope of Work
i. 12,381 Acres Aerial Survey using UAV along the PBRLP alignment from Dhaka to
Jessore.
ii. Establishment 835 Number GCP's using RTK GNSS,
iii. Data Processing and producing of Georeferenced DTM, DSM, Contour Map and
Orthophoto.
iv. Preparation of Web Tiles and Web portal to visualize the map.
v. Setup the Network for Web Portal.
Key Findings
i. Produced Orthophoto for 12,381 Acre area along the PBRLP alignment from Dhaka to
Jessore with 2 cm GSD.
ii. Collected GCP point Coordinates.
iii. Produced DEM, DSM, Contour Map, & Ortho mosaic map of the project area.
iv. Web tiles and web portal of the map.
v. Established network for Web Portal.
Jolshiri Abashon Project
Scope of Work
i. Aerial Survey for 2,240 acres of land using UAV in Jolshiri Abason area
ii. Establishment of GCP's using RTK GNSS
iii. Data Processing and producing of Georeferenced DTM, DSM, Contour Map and
Orthophoto.
Key Findings
i. Produced Orthophoto for 2,240 Acre area of Jolshiri Abason with 2 cm GSD
ii. Collected GCP point Coordinates.
iii. Produced DEM, DSM, Contour Map, & Ortho mosaic map of the project area.
BADC Deep Tubewells (DTWs) Survey project.
Project Description
Surveying more than 10,000 Deep Tubewells in 33 District of Mymensingh, Dhaka, Rangpur and Rajshahi Division with RTK GNSS.
Scope of Work
i. 10,000 DTWs survey through Real Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS
ii. Prepare digital data of all services, Serial/ID no, District, Upazila &
Upazila wise serial no for each DTW
iii. PField ID as found in the original data sheet provided by BADC.
iv. Latitude & Longitude (WGS 84) and Altitude in meter (MSL, PWD, Ellipsoid
Height)
v. Picture of the data measurement spot captured by smart phone for each DTW.
vi. Data in MS Excel sheet, GIS shape files and Geodatabase
Bangladesh Power Development Board (PDB) Pole Survey.
Project Description
Scope of Work